优秀装饰器源码学习(一):time
前言
最近又温习了一遍TS装饰器,准备用装饰器改造一下自己的轮子
在改造之前,准备先学习一下优秀的装饰器开源库,站在巨人的肩膀上前行
根据一些博文的推荐,就选择了core-decorators
准备工作
可将源码 clone到本地进行学习
也可直接利用github1s在线预览
搭建测试环境
全局安装ts-node与typescript两个依赖
sh
npm install ts-node typescript -g初始化ts配置文件(tsconfig.json)
sh
tsc --init将noImplicitAny,noImplicitThis设置为false,experimentalDecorators设置为true
json
{
"compilerOptions": {
/* Visit https://aka.ms/tsconfig.json to read more about this file */
"target": "es5",
"lib": ["ESNext","DOM"],
/* Strict Type-Checking Options */
"strict": true, /* Enable all strict type-checking options. */
"noImplicitAny": false,
"noImplicitThis": false, /* Raise error on 'this' expressions with an implied 'any' type. */
"esModuleInterop": true, /* Enables emit interoperability between CommonJS and ES Modules via
/* Experimental Options */
"experimentalDecorators": true, /* Enables experimental support for ES7 decorators. */
/* Advanced Options */
"skipLibCheck": true, /* Skip type checking of declaration files. */
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true /* Disallow inconsistently-cased references to the same file. */
}
}编写示例测试
ts
function defaultValue(str:string){
return function(target,property){
target[property] = str
}
}
class User {
@defaultValue('666')
private _name: string | undefined
constructor(name?:string) {
if(name){
this._name = name
}
}
get name(){
return this._name
}
}
const a = new User()
console.log(a.name); // 666运行,结果如上数的注释所示
ts
ts-node first.ts源码目录
简单数了一下大概有17个,咱一个个的挨着学,细细品
下面开始和大家一起学,由易到难
time
用于计算一个函数执行耗时
使用示例
使用如下,通过一个简单的 @time 即可让函数执行完后打印执行时间
ts
import { time } from './../index'
class Test {
@time()
sayHello() {
let i = 0
while (i < 100000) {
i++
}
console.log('success');
}
}
const t = new Test()
t.sayHello()执行效果
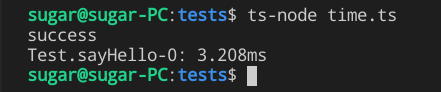
console.time实现
计算程序的执行时间可以利用console.time与console.timeEnd实现
ts
console.time('label')
// ...code
console.timeEnd('label') // 即可打印出执行耗时源码中为避免环境不支持console.time/timeEnd,巧妙实现了一下,源码如下
ts
const labels = {}
// 替代console.time
const myTime = (label) => {
// 记录开始时间
labels[label] = new Date().getTime()
}
// 替代console.timeEnd
const myTimeEnd = (label) => {
const timeNow = new Date().getTime();
// 当前时间与开始时间做差
const timeTaken = timeNow - labels[label];
// 删除无用的标志
delete labels[label];
// 打印耗时
console.log(`${label}: ${timeTaken}ms`);
}函数结构
传入参数:
- prefix:默认null
- 自定义console:默认使用内建的console.time/timeEnd
ts
// 首先是console.time的polyfill
// 当没定义time与timeEnd的时候,利用labels变量实现类似的效果
const defaultConsole = {
time: console.time ? console.time.bind(console) : myTime,
timeEnd: console.timeEnd ? console.timeEnd.bind(console) : myTimeEnd
}
// 用于label生成
let count = 0
export default function time(prefix: null | string = null, console = defaultConsole) {
return function (target, key, descriptor) {
}
}最终实现
ts
let count = 0
export default function time(prefix: null | string = null, console = defaultConsole) {
return function (target, key, descriptor) {
const fn = descriptor.value
// 如果没有传参
// 使用构造函数的名称与装饰对象的属性名作为key
if (prefix === null) {
prefix = `${target.constructor.name}.${key}`;
}
// 校验装饰对象是否为函数
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new SyntaxError(`@time can only be used on functions, not: ${fn}`);
}
return {
...descriptor,
value() {
const label = `${prefix}-${count}`
count++
console.time(label)
try {
return fn.apply(this, arguments)
} finally {
console.timeEnd(label)
}
}
}
}
}未完待续
本文主要介绍了测试环境的搭建,跟着源码一起重现了time函数
后续文章将直接对源码进行分析与学习

