优秀装饰器源码学习(二)
前言
上一篇文章:优秀装饰器源码学习(一):time
本篇先学习一些初级较简单的 @deprecate, @readonly, @enumerable, @nonconfigurable
deprecate
用于提示XX API/方法已经被弃用
使用示例
使用如下,通过一个简单的 @deprecate 即可在函数执行的时候抛出 API已被弃用的警告
其中 deprecate与deprecated效果一致,只是不同的别名
ts
export { default as deprecate, default as deprecated } from './core/deprecate'ts
import { deprecate, deprecated } from '../index'
class Test {
@deprecate()
sayHello1() {
console.log('hello 1');
}
@deprecated('API弃用警告')
sayHello2() {
console.log('hello 2');
}
@deprecate('API弃用警告',{url:'https://www.baidu.com'})
sayHello3() {
console.log('hello 3');
}
}
const t = new Test()
t.sayHello1()
t.sayHello2()
t.sayHello3()执行效果

函数结构
传入参数:
- msg:有默认内容
- options:通过url属性进一步指定文档链接
ts
const DEFAULT_MSG = 'This function will be removed in future versions.';
interface Options{
url?:string
}
export default function deprecate(msg = DEFAULT_MSG, options:Options = {}) {
return function (target, key, descriptor) {
}
}最终实现
ts
const DEFAULT_MSG = 'This function will be removed in future versions.';
interface Options{
url?:string
}
export default function deprecate(msg = DEFAULT_MSG, options:Options = {}) {
return function (target, key, descriptor) {
// 如果被装饰对象不是函数,直接抛出错误
if (typeof descriptor.value !== 'function') {
throw new SyntaxError('Only functions can be marked as deprecated');
}
// 生成方法的签名(反应来自与xx类xx方法)
const methodSignature = `${target.constructor.name}#${key}`;
// 如果有线上地址的文档描述原因,则展示一下这个地址
if (options.url) {
msg += `\n\n See ${options.url} for more details.\n\n`;
}
return {
...descriptor,
value: function deprecationWrapper() {
// 打印警告信息
console.warn(`DEPRECATION ${methodSignature}: ${msg}`);
// 执行函数
return descriptor.value.apply(this, arguments);
}
};
}
}readonly
将指定属性变为只读,即不可在实例化后更改属性的内容
使用示例
使用如下,通过一个简单的 @readonly 即可将目标属性变为只读
ts
import { readonly } from '../index';
class Test {
hello1(){
console.log('hello1');
}
@readonly
hello2(){
console.log('hello2');
}
}
const t = new Test();
t.hello1 = function(){
console.log('1');
}
t.hello1()
t.hello2 = function(){
console.log('2');
}
t.hello2()执行效果
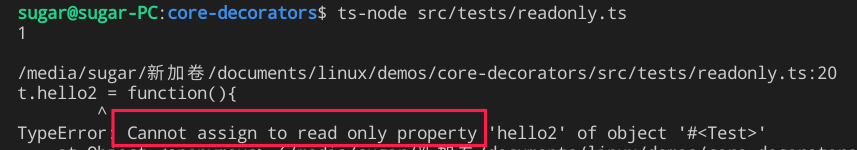
函数实现
无需额外传参,直接通过修改装饰对象的descriptor上的writable属性为false实现
ts
export default function readonly(target, key, descriptor) {
descriptor.writable = false
return descriptor
}enumerable、nonenumerable、enumable
更改装饰对象的enumerable属性值
使用示例
ts
import enumable from "../core/enumable";
import enumerable from "../core/enumerable";
import nonenumerable from "../core/nonenumerable";
class Test {
@nonenumerable
a(){
}
@enumerable
b(){
}
@enumable(false)
c(){
}
}
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(Test.prototype,'a')?.enumerable === false); // true
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(Test.prototype,'b')?.enumerable === true); // true
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(Test.prototype,'c')?.enumerable === false); // true
console.log(Object.keys(Test.prototype)); // ['b']实现
这个比较简单就是修改一下装饰对象的enumerable值
enumerable
ts
export default function enumerable(target, key, descriptor) {
descriptor.enumerable = true
return descriptor
}nonenumerable
ts
export default function nonenumerable(target, key, descriptor) {
descriptor.enumerable = false
return descriptor
}enumable
ts
export default function enumable(v = true) {
return function (target, key, descriptor) {
descriptor.enumerable = v
return descriptor
}
}nonconfigurable
设置装饰对象的configurable属性为false
当且仅当 configurable 为 true 时,该属性的描述符才能够被改变,同时该属性也能从对应的对象上被删除。
使用示例
ts
import { nonconfigurable } from "../index";
class Test {
@nonconfigurable
a(){
}
b(){
}
}
let prototype:any = Test.prototype
delete prototype.b
console.log(Object.keys(Test.prototype)); // ['a']
delete prototype.a // 抛出错误: Cannot delete property 'a' of #<Test>
console.log(Object.keys(Test.prototype));实现
这个依旧比较简单就是修改一下装饰对象的configurable值
ts
export default function nonconfigurable(target, key, descriptor) {
descriptor.configurable = false
return descriptor
}未完待续
下一篇将学习:
@mixin:混入方法到类中@lazyInitialize:在使用的时候才初始化目标属性@debounce:防抖@throttle:节流

